Table of Contents
Graph
A graph G is mathematical structure consisting of two set V and E where V is non-empty set of vertices & E is a non-empty set of edges.
Example
Types of Graph
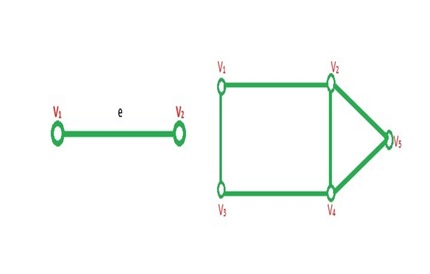
1-Trivial Graph: A graph consisting only one vertex and edge.
Example

2-Mull Graph: A graph consisting. n vertices and no edge.
Example

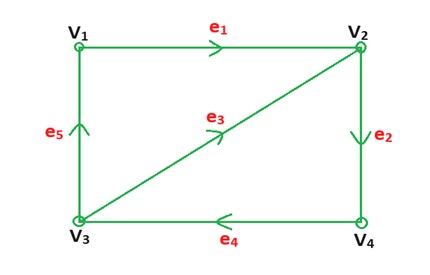
3-Directed Graph: A graph consist the direction of edges then this is called directed graph.
Example
4-Unidirected Graph: A graph which is not directed then it is called undirected graph.
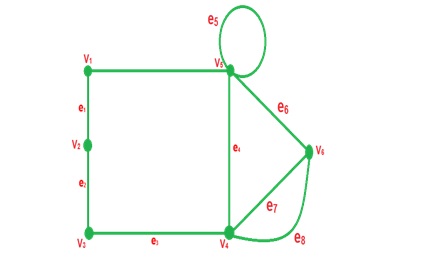
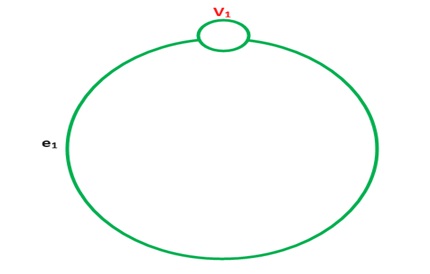
5-Sey loop in a Graph: if edge having the same vertex as both its end vertices is called self loop.
Example
6-Proper edge: An edge which is not self loop is called proper edge
Example

7-Multi edge: A collection of two or more edges having indentically end point.
Example
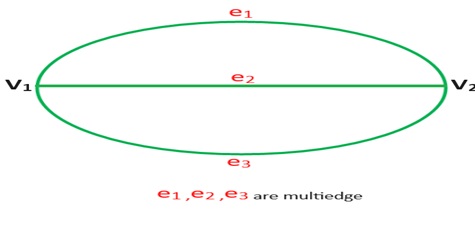
8-Simple Graph: A graph does not contain and any self loop and multiedge.
Example
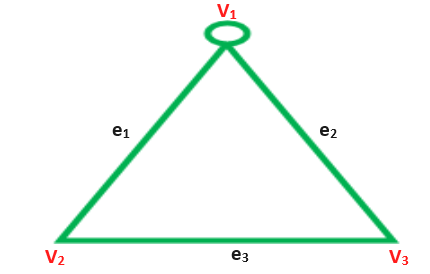
9-Multigraph: A graph does not contain any self loop but contain multiedge is called multigraph.
Example
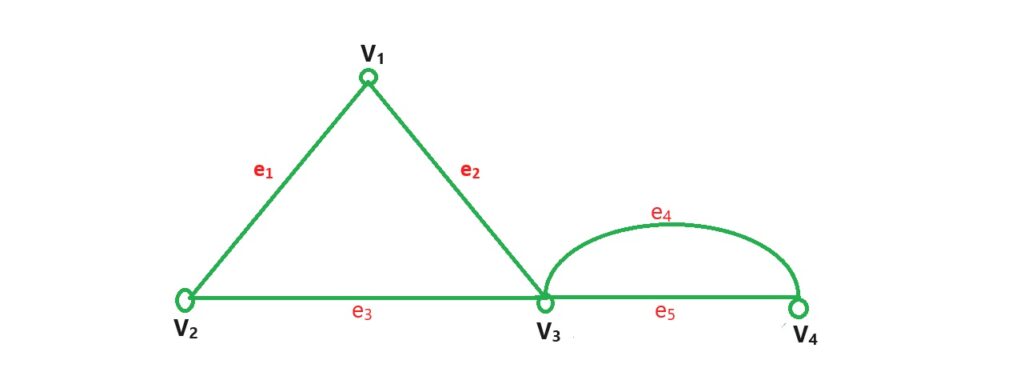
10-Pseudo Graph: A graph contain both sey loop and multiedge is Called pseudo Graph
Example